字符串
字符串变量声明
用引号(单引号或双引号)括起来,可以包含字母、数字和特殊字符。
a = "Hello, World!"
b = 'Python is cool'空字符串:
my_string = ""多行字符串
可以通过将文本括在三引号中来创建多行字符串,即三个单引号 (''') 或三个双引号 (""").
multiline_string = '''
This is a multiline string
that spans multiple lines.
You can use single quotes
or double quotes.
'''
print(multiline_string)注意
请注意,三引号字符串中的任何空白,包括换行符,都将包含在字符串中。如果您想排除行首或行尾的空白,可以使用 strip() 或 rstrip() 等字符串方法。
字符串连接
字符串连接是将两个或多个字符串组合成一个字符串的过程。在 Python 中,你可以使用 + 运算符连接字符串。
str1 = "Hello"
str2 = "World"
result = str1 + " " + str2
print(result) # Output: Hello World附加字符串的另一种选择是使用 += 运算符。
list = ["Hello", "World"]
result = ""
for item in list:
result += item
print(result)
# 输出:HelloWorld字符串中的变量
字符串连接
可以使用 + 运算符连接字符串和变量
name = "Alice"
age = 30
message = "Hello, my name is " + name + " and I am " + str(age) + " years old."
print(message)使用 str.format() 方法
使用占位符 {} 在字符串中嵌入变量
name = "Bob"
age = 25
message = "Hello, my name is {} and I am {} years old.".format(name, age)
print(message)使用 f 字符串
name = "Charlie"
age = 35
message = f"Hello, my name is {name} and I am {age} years old."
print(message)字符串长度
使用内置函数 len() 获取字符串的长度,还可以使用此方法检查字符串是否为空。
my_string = "Hello, world!"
print(len(my_string)) # Output: 13empty_string = ""
print(len(empty_string)) # Output: 0
whitespace_string = " "
print(len(whitespace_string)) # Output: 3字符串比较
在 Python 中比较字符串时,比较是按字典顺序进行的,这意味着比较基于字符串中字符的 ASCII 值。
== 运算符
检查两个字符串是否相等。
str1 = "mango"
str2 = "pineapple"
if str1 == str2:
print("相等")
else:
print("不相等")
# 输出: 不相等!= 运算符
检查两个字符串是否不相等。
str1 = "mango"
str2 = "pineapple"
if str1 != str2:
print("不相等")
else:
print("相等")
# 输出:不相等< 运算符
检查第一个字符串在词典顺序中是否小于第二个字符串。
str1 = "mango"
str2 = "pineapple"
if str1 < str2:
print("str1 小于 str2")
else:
print("str2 大于等于 str1")
# 输出:str1 小于 str2> 运算符
检查第一个字符串在词典顺序中是否大于第二个字符串。
<= 运算符
检查第一个字符串是否小于或等于第二个字符串(按字典顺序)。
>= 运算符
检查第一个字符串是否大于或等于第二个字符串(按字典顺序)。
字符串遍历
使用 for 循环
my_string = "Hello, world!"
for char in my_string:
print(char)使用 while 循环
my_string = "Hello, world!"
i = 0
while i < len(my_string):
print(my_string[i])
i += 1使用列表解析
my_string = "Hello, world!"
char_list = [char for char in my_string]
print(char_list)
# 输出:['H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ',', ' ', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!']使用 map() 函数
my_string = "Hello, world!"
char_list = list(map(str, my_string))
print(char_list)使用 enumerate() 函数
my_string = "Hello, world!"
for index, char in enumerate(my_string):
print(f"Character at index {index}: {char}")字符串大小写转换
lower() 和 upper() 方法分别用于将字符串中的所有字符转换为小写和大写。
lower() 方法将字符串中的所有大写字符转换为相应的小写字符,同时保留所有现有的小写字符。
string = "Hello World"
new_string = string.lower()
print(new_string) # Output: hello worldupper() 方法将字符串中的所有小写字符转换为相应的大写字符,同时保留所有现有的大写字符。
string = "Hello World"
new_string = string.upper()
print(new_string) # Output: HELLO WORLD字符串首字母大写
capitalize() 方法仅将字符串的首字母大写,并将其余字母保留为小写。
string = "hello world"
capitalized_string = string.capitalize()
print(capitalized_string) # Output: Hello world字符串替换
replace() 方法
string = "Hello World"
new_string = string.replace("Hello", "Hi")
print(new_string) # Output: Hi World删除换行符
string_with_newline = "This is a string\nwith a newline character."
string_without_newline = string_with_newline.replace("\n", "")
print(string_without_newline) # Output: This is a stringwith a newline character.在上面的代码中,我们首先定义了一个名为 string_with_newline 的字符串,其中包含一个换行符 (\n)。然后我们使用 replace() 方法用空字符串 ("") 替换换行符的所有出现。结果字符串 string_without_newline 不包含任何换行符。然后我们使用 print() 函数打印结果字符串。
strip() 方法
strip() 方法可用于删除空格字符,如空格、制表符和换行符。
string = " hello world "
new_string = string.strip()
print(new_string) # Output: "hello world"如果只想删除前导或尾随空格,则可以使用 lstrip() 或 rstrip() 方法。
字符串切片
字符串切片是从现有 Python 中的字符串 创建新子字符串的过程。你可以使用语法 [start:end] 切片字符串,以提取字符串中从 start 索引开始到 end 索引结束(不包括)的部分。
my_string = "Hello, world!"
# 索引 0 到 4 (不包含4)获取子字符串
print(my_string[0:4]) # 输出: "Hell"
# 索引从 7 到末尾获取子字符串
print(my_string[7:]) # 输出: "world!"
# 索引从 2 到 12 (不包含12) 步进 2 获取子字符串
print(my_string[2:12:2]) # 输出: "lo ol"
# 索引从 2 到倒数第一个(不包含倒数第一个)获取子字符串
print(my_string[2:-1]) # 输出: "llo, world"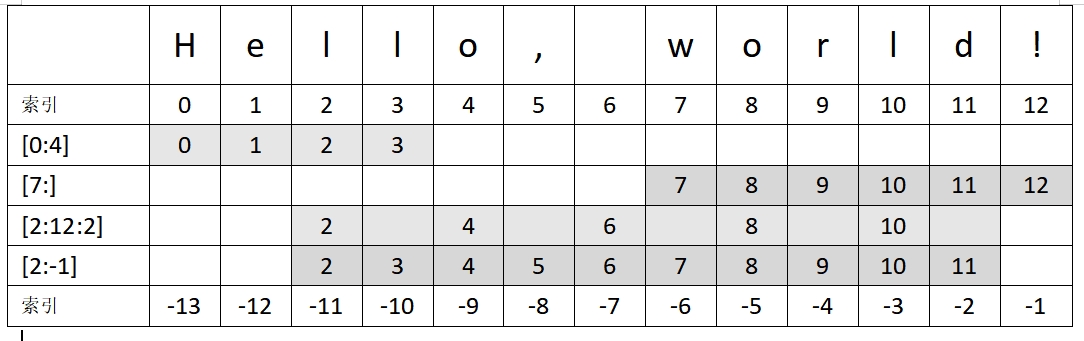
要使用分隔符拆分字符串,你还可以使用 split() 方法。
my_string = "Hello,world"
my_list = my_string.split(",")
print(my_list) # Output: ['Hello', 'world']以使用字符串切片从 Python 中的字符串中删除第一个字符。
string = "hello"
new_string = string[1:]
print(new_string) # Output: ello字符串切片还可以用来从字符串中删除最后一个字符。
my_string = "Hello World!"
new_string = my_string[:-1]
print(new_string) # Output: "Hello World"字符串子集
要检查 Python 字符串是否包含特定子字符串,你可以使用 in 关键字或 find() 方法。
in 关键字
my_string = "Hello, world!"
if "world" in my_string:
print("Substring found!")
else:
print("Substring not found.")
# Output: Substring found!find() 方法
这是内置 Python 函数,它返回给定字符串中子字符串首次出现的索引。如果找不到子字符串,它将返回 -1。
my_string = "Hello, world!"
if my_string.find("world") != -1:
print("Substring found!")
else:
print("Substring not found.")
# Output: Substring found!字符串反转
使用切片
string = "hello"
reversed_string = string[::-1]
print(reversed_string) # Output: "olleh"使用 reversed() 函数
string = "hello"
reversed_string = "".join(reversed(string))
print(reversed_string) # Output: "olleh"使用循环
string = "hello"
reversed_string = ""
for char in string:
reversed_string = char + reversed_string
print(reversed_string) # Output: "olleh"字符串截断
text = "This is a long text that needs to be truncated."
max_length = 20
truncated_text = text[:max_length] + "..." if len(text) > max_length else text
print(truncated_text) # Output: This is a long text...使用切片获取字符串的前 max_length 个字符。如果原始字符串的长度大于 max_length,我们使用字符串连接在截断字符串的末尾追加省略号。如果原始字符串的长度小于或等于 max_length,我们只需将原始字符串分配给 truncated_text 变量。
startswith() 和 endswith() 方法
startswith() 方法用于检查字符串是否以特定前缀开头。该方法将一个或多个前缀作为参数,如果字符串以其中任何一个前缀开头,则返回 True,否则返回 False。以下是 startswith() 方法的语法
string.startswith(prefix, start=0, end=len(string))其中
prefix是要检查的前缀。start是一个可选参数,指定要搜索的字符串的起始索引。默认情况下,start设置为 0,这意味着将搜索整个字符串。end是一个可选参数,指定要搜索的字符串的结束索引。默认情况下,end设置为字符串的长度。
s = "Python is a great programming language"
print(s.startswith("Python")) # True
print(s.startswith("Java")) # False
print(s.startswith(("Java", "Python"))) # True (checking multiple prefixes)endswith() 方法用于检查字符串是否以特定后缀结尾。该方法将一个或多个后缀作为参数,如果字符串以其中任何一个结尾,则返回 True,否则返回 False。以下是 endswith() 方法的语法
string.endswith(suffix, start=0, end=len(string))其中
suffix是要检查的后缀。start和end参数与startswith()方法中的含义相同。
下面是使用 endswith() 方法的一个示例
s = "Python is a great programming language"
print(s.endswith("language")) # True
print(s.endswith("Python")) # False
print(s.endswith(("Python", "language"))) # True (checking multiple suffixes)count() 方法
可以使用内置的 count 方法计算字符串中子字符串出现的次数。
string = "Hello, world! This is a sample string."
substring = "is"
count = string.count(substring)
print(count) # Output: 2转换为字符串
要将非字符串对象转换为 Python 中的字符串),可以使用 str() 函数。
# convert an integer to a string
num = 42
str_num = str(num)
print(str_num) # outputs "42"
print(type(str_num)) # outputs "<class 'str'>"
# convert a float to a string
pi = 3.14159
str_pi = str(pi)
print(str_pi) # outputs "3.14159"
print(type(str_pi)) # outputs "<class 'str'>"
# convert a boolean to a string
flag = True
str_flag = str(flag)
print(str_flag) # outputs "True"
print(type(str_flag)) # outputs "<class 'str'>"Unicode 转换为字符串
可以使用 encode 方法将 Unicode 字符串转换为常规字符串(也称为字节字符串)。
unicode_string = "Hello, World! 🌍"
byte_string = unicode_string.encode("utf-8")
print(byte_string) # Output: b'Hello, World! \xf0\x9f\x8c\x8d'请注意,输出中的 b 前缀表示该值是字节字符串,而不是常规字符串。如果你想将字节字符串转换回常规字符串,可以使用 decode 方法。
new_unicode_string = byte_string.decode("utf-8")
print(new_unicode_string) # Output: Hello, World! 🌍字符串转换为列表
使用内置的 list() 函数
my_string = "hello"
letters_list = list(my_string)
print(letters_list)循环遍历字符串并将每个字母追加到新列表中
my_string = "hello"
letters_list = []
for letter in my_string:
letters_list.append(letter)
print(letters_list)字符串转换为布尔值
可以使用内置的 bool() 函数将字符串转换为布尔值。
默认情况下,以下字符串被视为 True
- 任何非空字符串
- 字符串“True”(不区分大小写)
另一方面,以下字符串被视为 False
- 空字符串
- 字符串“False”(不区分大小写)
- 任何等于 0 的数字值(即“0”或“0.0”)
>>> bool("hello")
True
>>> bool("")
False
>>> bool("True")
True
>>> bool("false")
False
>>> bool("0")
False
>>> bool("1")
True字符串转换为十六进制
可以使用 encode() 方法和 'hex' 编码将字符串转换为其十六进制表示形式。
string = "Hello, world!"
hex_string = string.encode('hex')
print(hex_string) # Output: 48656c6c6f2c20776f726c6421在 Python 3 中,可以使用 hex() 方法将字符串转换为其十六进制表示形式。
string = "Hello, world!"
hex_string = ''.join([hex(ord(c))[2:] for c in string])
print(hex_string) #Output: 48656c6c6f2c20776f726c6421// TODO
join() 方法
此方法允许你使用分隔符字符串将可迭代对象(例如列表、元组或字符串)的元素连接到单个字符串中。
my_list = ['mango', 'pineapple', 'banana']
separator = ', '
result = separator.join(my_list)
print(result) # Output: "mango, pineapple, banana"二进制字符串
可以使用前缀 0b 后跟一系列 0 和 1 数字来表示二进制字符串。例如,二进制字符串 1101 可以表示为 0b1101。
创建二进制字符串
binary_str = '0b1101'将十进制整数转换为二进制字符串
decimal_num = 13
binary_str = bin(decimal_num)将二进制字符串转换为十进制整数
binary_str = '0b1101'
decimal_num = int(binary_str, 2)二进制字符串上的按位运算
binary_str1 = '0b1101'
binary_str2 = '0b1010'
# Bitwise AND
result = int(binary_str1, 2) & int(binary_str2, 2)
print(bin(result)) # Output: 0b1000
# Bitwise OR
result = int(binary_str1, 2) | int(binary_str2, 2)
print(bin(result)) # Output: 0b1111
# Bitwise XOR
result = int(binary_str1, 2) ^ int(binary_str2, 2)
print(bin(result)) # Output: 0b0111请注意,在执行按位运算时,我们需要使用 int() 函数将二进制字符串转换为十进制 整数,其中第二个参数指定基数(在本例中为 2),然后使用 bin() 函数将结果转换回二进制字符串。
参考:
Python 中的字符串变量:声明、连接、长度、比较 - 《Dive into Python》中文版
Python 中字符串规范化方法 - 小写、大写和首字母大写 - 《Dive into Python》中文版
Python 中的字符串替换:替换子字符串和字符 - 《Dive into Python》中文版
Python 中的子字符串操作:切片、子集、反转、拆分、替换 - 《Dive into Python》中文版
[字典序_百度百科](https://baike.baidu.com/item/字典序/7786229