In this blog, we will learn how to work with the OkHttp Interceptors. We will also see the real use cases where we can use it and how we can use it to get the most of it. In Android, we have so many use-cases that can be done using the OkHttp Interceptors.
Today, we will cover the following sections to master it:
- What are Interceptors?
- Types of Interceptors.
- How to add Interceptors in OkHttpClient?
- Creating the Interceptor.
- Real use-cases using the Interceptors.
What are Interceptors?
According to documentation, Interceptors are a powerful mechanism that can monitor, rewrite, and retry the API call. So basically, when we do some API call, we can monitor the call or perform some tasks.
In simple words, Interceptors are like the security personnel in the security check process at the Airport. They check our boarding pass, put a stamp on it and then would allow us to pass.

We can use the interceptors to do so many things, for example, monitor the API calls centrally. Generally, we need to add the logger for each network call, but by using the interceptor, we can add one logger centrally and that will work for all the network calls. Another use-case can be caching the response of network calls to build the offline-first app, we will learn it later in this blog in detail.
Types of Interceptors
We have two types of interceptors as follows:
- Application Interceptors: These are interceptors that are added between the Application Code(our written code) and the OkHttp Core Library. These are the ones that we add using addInterceptor().
- Network Interceptors: These are interceptors that are added between the OkHttp Core Library and the Server. These can be added to OkHttpClient using addNetworkInterceptor().
How to add interceptors in OkHttpClient?
While building the OkHttpClient object, we can add the interceptor like below:
1 | fun myHttpClient(): OkHttpClient { |
Here, in addInterceptor we pass the interceptor that we have created. Now, let’s see how to create the Interceptor.
Creating the Interceptor
To create the interceptor, we need to create a class by implementing the Interceptor interface like below:
1 | class MyInterceptor : Interceptor { |
Here, in the intercept(), we can perform any action which we want inside it.
And to use the interceptor, we can use like below:
1 | fun myHttpClient(): OkHttpClient { |
We can add the MyInterceptor in addInterceptor().
Now, let’s discuss more real use-cases where we can use the Interceptors.
Real use-cases using the Interceptors
The following are the common use-cases in Android:
Logging the errors centrally
First, we need to create the ErrorInterceptor like below:
1 | class ErrorInterceptor : Interceptor { |
- First, we get the request from chain.request()
- Then, we get the response returned from the server, by passing the request in chain.proceed(request)
- Now, we can check for the response code and perform an action.
- We can pass the error to the view using via the interfaces or by using something like RxJava, EventBus, and etc.
- Let’s say if we get a 401 error i.e. Unauthorized then we can perform an action to clear the app data/log out the user or any action which we want to perform.
Now, to use this ErrorInterceptor in our OkHttpClient, we can add like below:
1 | .addInterceptor(ErrorInterceptor()) |
This is how we can create a centralized Error Logger using the Interceptor.
OkHttp has a built-in logger which is very useful for debugging.
To learn more about the built-in logger, click here.
Note: If we want to log the details for the redirection of URL, consider using the interceptor at the network layer using the addNetworkInterceptor().
Caching the response
If we want to cache the response of the API call so that if we call the API again, the response comes out from Cache.
Let’s say we have the API call from Client to Server and Cache-Control header is enabled from the server, then OkHttp Core will respect that header and cache the response for a certain time being which was sent from the server.
But what if the Cache-Control is not enabled from the server. We still can cache the response from OkHttp Client using Interceptor.
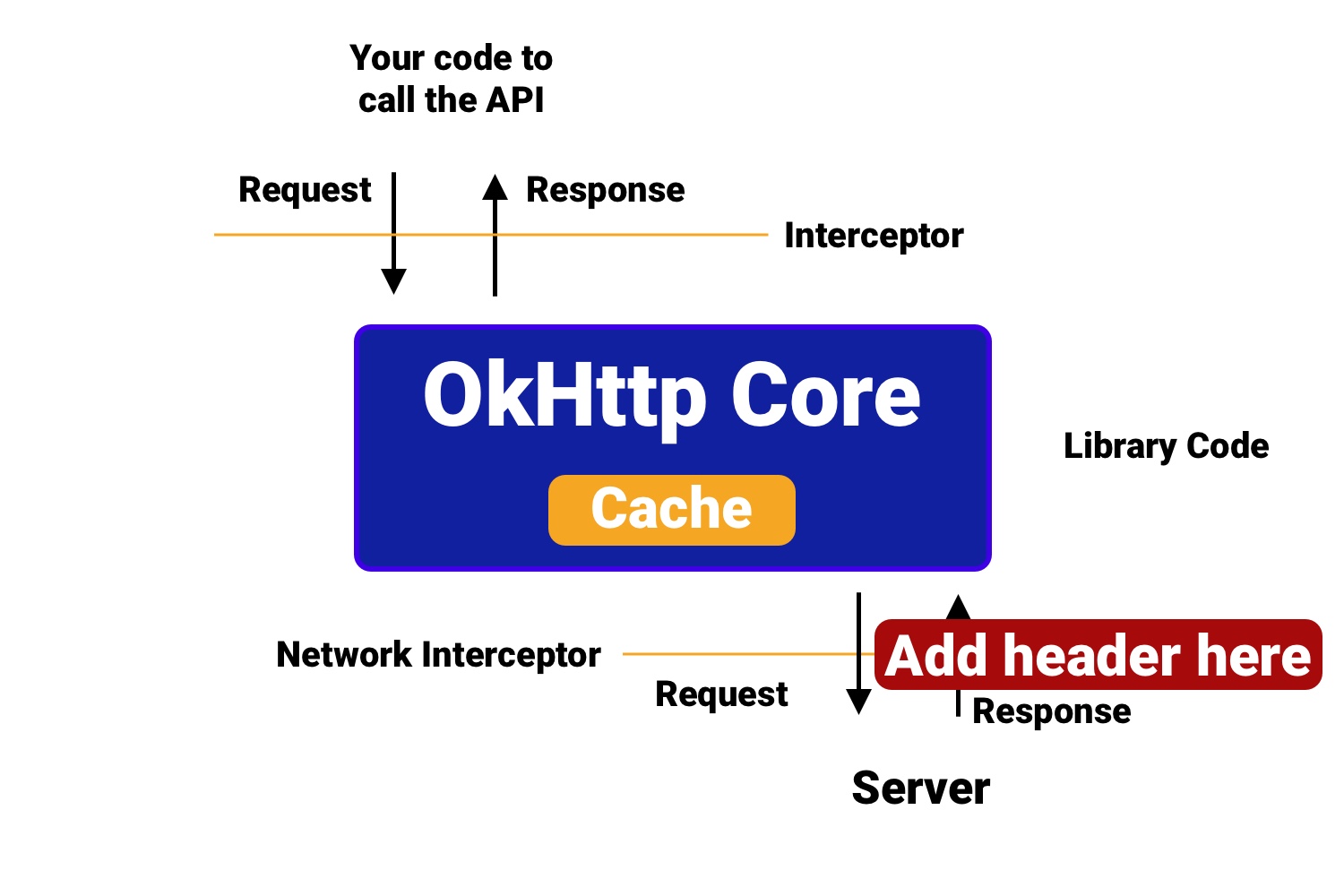
Just see the above image. Here, what we have to do is that we have to intercept the Response before going inside the OkHttp Core and add the header (Cache-Control), so it will be treated as if the response(with the Cache-Control header) has come from the server, and OkHttp Core will respect that and cache the response.
We will create an interceptor like below:
1 | class CacheInterceptor : Interceptor { |
Here, we have a CacheControl which is used to provide the header for Cache-Control.
Finally, we can add like below:
1 | .addNetworkInterceptor(CacheInterceptor()) |
Here, if we see, we are not using the addInterceptor() but using addNetworkInterceptor() for the use case. This is because in this case, the operation is happening at the network layer.
But, there is something important, we need to consider while building the offline-first app.
The cached response will be returned only when the Internet is available as OkHttp is designed like that.
- When the Internet is available and data is cached, it returns the data from the cache.
- Even when the data is cached and the Internet is not available, it returns with the error “no internet available“.
What to do now?
We can use the following ForceCacheInterceptor at the Application layer in addition to the above one (CacheInterceptor, only if not enabled from the server). To implement in the code, we will create a ForceCacheInterceptor like below:
1 | class ForceCacheInterceptor : Interceptor { |
We can add the Interceptor in OkHttpClient like below:
1 | .addNetworkInterceptor(CacheInterceptor()) // only if not enabled from the server |
Here, we are adding the ForceCacheInterceptor to OkHttpClient using addInterceptor() and not addNetworkInterceptor() as we want it to work on the Application layer.
Adding the Header like Access Token centrally
Let’s say that we have to make the API calls and we have to add Authorization Header in all the API calls. Either we can use it individually or we can centralize that using the Interceptor.
1 | class AuthTokenInterceptor : Interceptor { |
- First, we get the token for the header from our local storage like a SharedPreference.
- Here, we intercept the original request which we triggered from the application using chain.request() and set it to originalRequest.
- Then, we build the request again by adding the Header with the key and value which is required to make the network call.
- Then, we will build the request again and return the response using chain.proceed(request) by passing the new request which is having the Authorization header.
This is how we can centralize the Header which is common in all the API Calls. Now to use it in the OkHttpClient, we will do like below:
1 | .addInterceptor(AuthTokenInterceptor()) |
Let’s go to another use-case.
Refreshing the Access Token at Single Place
Let us say we have a use-case that when we get a 401 error in the Error Interceptor and we need to refresh the auth token as we have an Unauthorized error. We can do that using the below:
1 | override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response { |
- If we get the response.code() as 401 i.e. Unauthorized, we will refresh the token here, then modify the request by adding the new header and make the new request to the server.
Note: Another way that is more flexible when it comes to refreshing the Access Token is to use the Authenticator interface of OkHttp.
Now, let’s move to another use-case.
Enabling Gzip at Android End
Gzip is used for data compression. In Android as well, we can use the Gzip for the compression using the interceptor.
So, while getting a response, OkHttp automatically respects the header (content encoding) and decompresses the data and returns, but let’s say when we have to send compressed data to a server, then we have to write our own interceptor.
We can find the GzipRequestInterceptor class here.
To use the interceptor we can use like below:
1 | .addInterceptor(GzipRequestInterceptor()) |
So, these are the real use-cases, how can we use the interceptors in our Android App. We can do a lot of things with interceptors. Let’s start making the most of it.
来源:
https://blog.mindorks.com/okhttp-interceptor-making-the-most-of-it